
Alchemy is the process of transmuting base elements to obtain something valuable, usually transforming base metal to obtain gold. However the production of gold for its material benefits has never been the true aim of alchemy. At its most pure, alchemy is a symbolic activity, an allegory of the process whereby humanity’s base nature is transformed into a pure and untainted state.
Alchemists think of their activity as a sacred science that penetrates nature. Alchemy is loaded with archetypal symbols and processes referring to different types of transformation. These concepts include the four elements of ancient tradition: fire, air, water and earth; and the seven main stages of the Great Work: Calcination, Dissolution, Separation, Conjunction, Fermentation, Distillation, and Coagulation.
It has long been thought that alchemy originated in Egypt (known to the ancients as Khem, Al-Khem in Arabic), but the practices of alchemy can be found in all civilisations.
Alchemy has long been associated with striking graphic visual art. Many of the sacred images in ancient Egyptina are alchemical in nature – that is, they embed occult (secret) meanings in their visual symbolism.
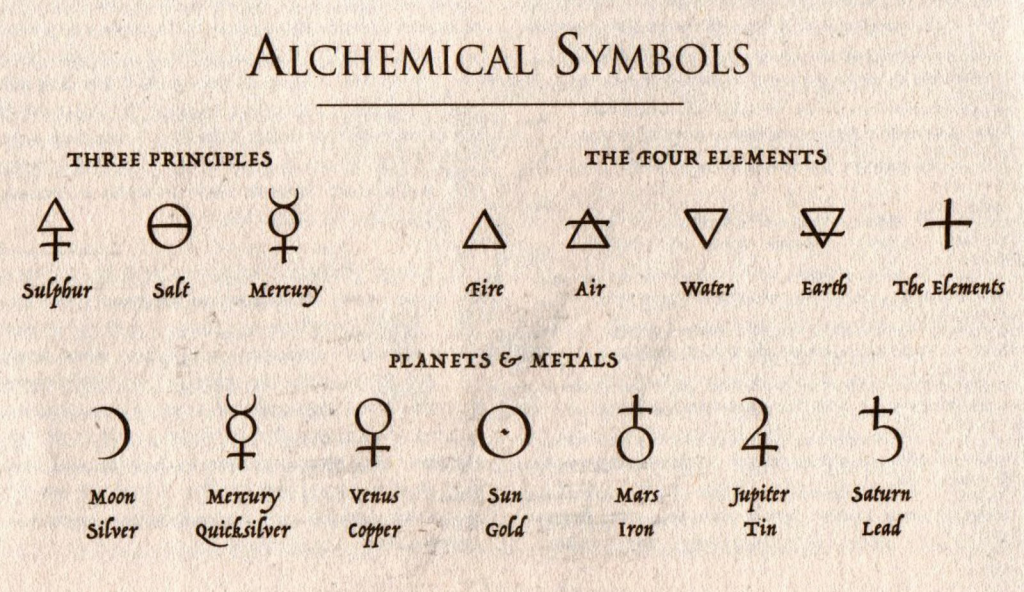
In European alchemy, this remained the case well into the 19th century. Instead of writing their formulae, alchemists would represent their knowledge with complex visual symbolism. Additionally, sigils ( a type of symbol used in magic, usually a pictorial signature of a deity or spirit) were represented in alchemical art.



